What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds
From cooking gas to the sugar in lemonade from the oxygen we inhale to the exhalation of carbon dioxide all consist of compounds containing covalent bonds. Atoms share their electrons in order to completely fill up their outer-most layer the valence shell.
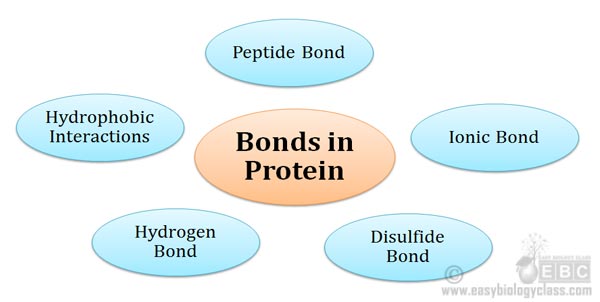
Chemical Bonds In Protein Biochemistry Notes Easy Biology Class
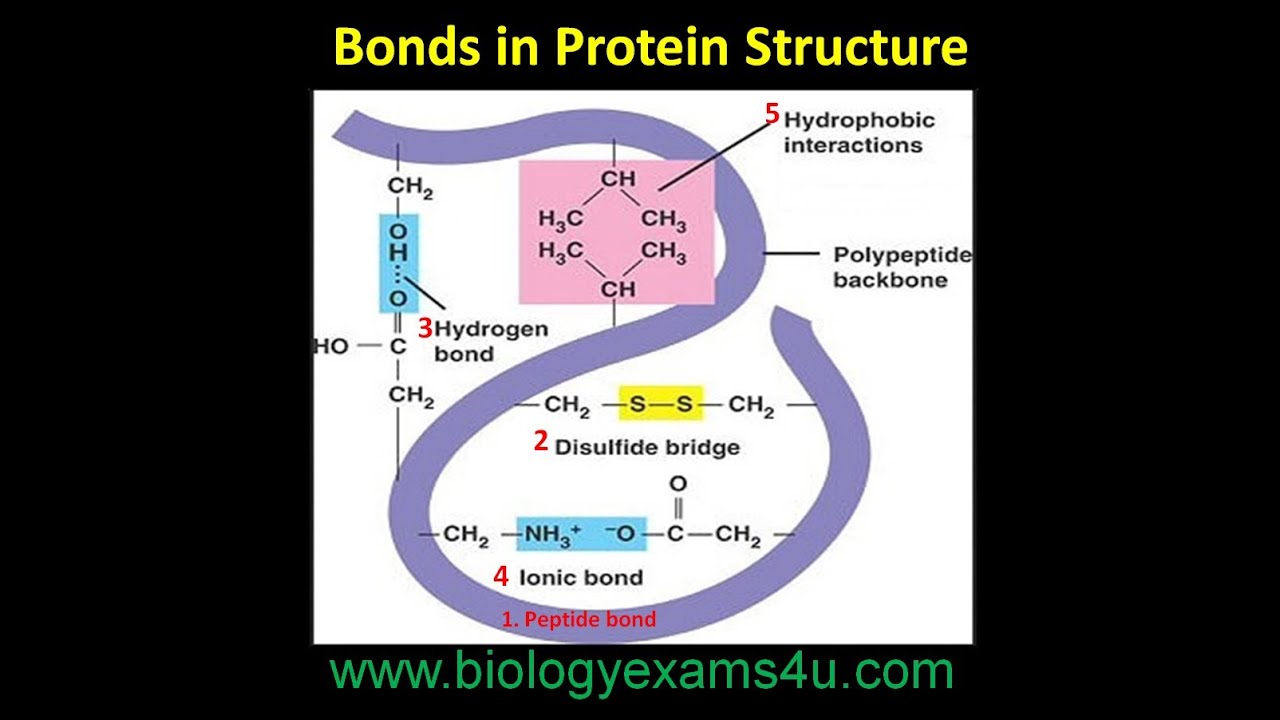
Covalent disulfide bonds formed between two cysteine residues contribute another fundamental type of linkage providing more stability and selectivity than noncovalent interactions.
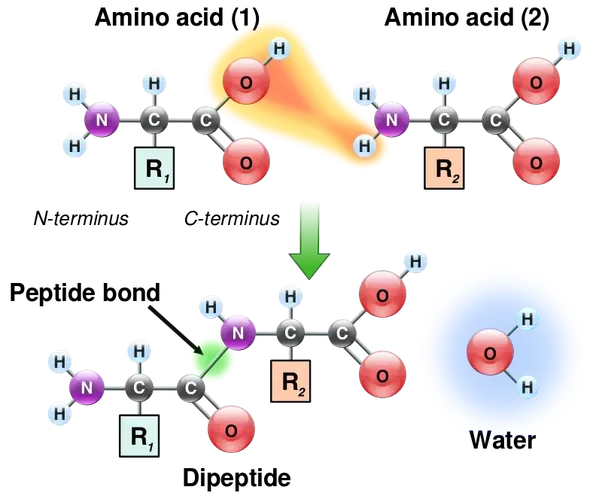
. Carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleus acids. Peptide Bonds. You can recognize these compounds because they consist of nonmetals bonded to each other.
Name the four categories of oganic molecules which form the basis of all living things. 1 Longer polymers 2 water released. A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
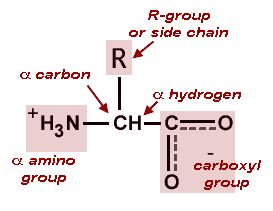
Covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules such as H 2 O CO 2 and O 2. Models have led to performance innovations in catalysis secondary ion batteries super-condensation drug delivery and molecular sieve offering easy paths to maximise form-oriented MOF surface areas. Amino acids themselves are made of atoms joined together by covalent bonds.
4 types of macromolecules. Covalent compounds also are known as molecular compounds. Dipeptide bonds is the specific name for the covalent bonds.
What molecules form proteins when linked with covalent bonds Understanding Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides Amino acids can be covalently joined together in a condensation reaction to form a dipeptide and waterThe covalent bond between the amino acids is called a peptide bond and for this reason long chains of covalently bonded. What molecules form protiens when linked together with covalent bonds. The primary structure of a protein consists of amino acids chained to each other.
What determines the shape and function of a protein. From the water used to boil an egg to the protein present inside it all are compounds having a covalent bond. The most common is a disulfide bond between the sulfur atoms of two cysteines.
Oils waxes proteins and starch. One two or three pairs of electrons may be shared between two. Covalent peptide bonds in the backbone and noncovalent interactions among amino acid side chains provide the essential framework for protein structure and function.
-long chain of identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. What molecules form protiens when linked together with covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules such as DNA and proteins.
Dipeptide bonds is the specific name for the covalent bonds. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids exactly the same from one molecule to the next. Amino acids are the molecules.
Coordinate covalent bonds involve the unequal sharing of an electron pair by two atoms with both electrons originally coming from the same atom. Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. One two or three pairs of electrons may be shared making single double and.
Amino acids are the molecules. Covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules like H 2 O CO 2 and O 2. Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules such as our DNA and proteins.
The -CONH- bond between amino acids is known as a peptide bond because relatively short polymers of amino acids are known as peptides. A large molecule that forms when many smaller molecules are linked together by covalent bonds. These are examples of covalent bonds and covalent compounds.
Proteins are formed by joining the -CO 2 H end of one amino acid with the -NH 2 end of another to form an amide. The electron pair donor is the ligand or Lewis base whereas the acceptor is the. If the atoms that form a covalent bond are identical as in H 2 Cl 2 and other diatomic molecules then the electrons in the bond must be shared equallyWe refer to this as a pure covalent bondElectrons shared in pure covalent bonds have an equal probability of being near each nucleus.
These bonds are stronger and much more common than are ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. Amino acids are organic molecules that contain amino group and carboxyl group. Proteins are therefore also known as polypeptides.
Which of the following biological molecules isare linked by covalent bonds formed by the removal of the elements of water from the reactants a kind of condensation reaction. Covalent bonds form when atoms share their valence electrons with other atoms to become a more stable molecule. Examples of important covalent bonds are peptide amide and disulfide bonds between amino acids and CC CO and CN bonds within amino acids.
Network covalent structures or giant covalent structures contain large numbers of atoms linked in sheets such as graphite or 3-dimensional structures such as diamond and. Cells join smaller carbon molecules to form larger carbon molecules Or. Two atoms that are covalently bonded have less energy than the individual atoms making the bonded atoms more stable.
A fat is most closely related to. These are most common in extracellular proteins. Amino acids link with each other by mean of peptide bonds covalent chemical bond and form proteins as a result.
Organic compounds such as carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids are all examples of molecular compounds. Some proteins are cross-linked with covalent bonds. A protein molecule is made from a long chain of these amino acids each linked to its neighbor through a covalent peptide bond.
Macromolecular structures have large numbers of atoms linked by covalent bonds in chains including synthetic polymers such as polyethylene and nylon and biopolymers such as proteins and starch. Sequence and shape of the amino acids R group. The same -CONH- bond forms the backbone of both proteins and synthetic fibers such as Nylon.
Compounds containing covalent bonds are part and parcel of our day-to-day life.
What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds Socratic
Bonds In Protein Structure Youtube

What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds Socratic

0 Response to "What Molecules Form Proteins When Linked With Covalent Bonds"
Post a Comment